
Resources management (water, energy, waste)
“In keeping with the spirit of craftsmanship, we manage natural resources responsibly and sparingly.”
Axel Dumas, Executive Chairman of Hermès
Ambition
Thanks to its artisanal model and innovative spirit, Hermès is able to develop while maintaining a low energy footprint and low levels of water consumption and waste production. Managing this consumption, which is integral to the company’s ecological and economic responsibility towards the major issues the planet currently faces, is an objective shared by all the company’s divisions and métiers.
The Group policy is based on the following pillars:
- Improving measurement of consumption in order to implement solutions for reduction;
- Improving production processes by favouring the most economical technologies;
- Innovating by making use of environmentally friendly solutions.
Organisation
Environmental matters, in particular water, energy and waste, are overseen by the Sustainable Development Committee and, more specifically, by the member of the Executive Committee responsible for the upstream division, supported by a Deputy Managing Director in charge of industrial affairs and by the real estate development department. Each year, an analysis of the main challenges takes place and is shared with the Executive Committee. Material recycling is overseen by a group committee made up of members of the main entities concerned: leather goods, textiles, ready-to-wear and the commercial division.
Water
Water for industrial use is mainly used in the tanneries and textile units. The Group consumes 608 megaliters of water per year.
Objectives
- To decouple industrial water consumption from increased business activity.
- To reduce industrial water consumption by 5% per year (m3 per million euros of turnover, constant scope) over the period 2018 to 2023.
- To implement a multi-stakeholder approach and co-build with external stakeholders (regional governments, authorities and professional associations).
Results 2023
- Hermès received an A rating from CDP for Water, illustrating the extent of the company’s efforts, in particular on an operational level.
- A specific water risk analysis, using the Water Risk Filter tool and in partnership with the WWF France, is currently underway on the company’s production sites and those of its main suppliers.
Evolution of industrial water consumption (m3)
In 2023, overall water consumption for industrial use decreased (-9.3%) compared to 2022, despite the impact of the integration of new sites in the reporting scope (decrease of 10% at constant scope). This is the result of continued reduction efforts on all the Group’s manufacturing sites. Over the past 10 years, the Group has maintained its aim of decoupling, with industrial water consumption increasing by a factor of 1.2 while activity grew 3.3 fold.
- -62%
reduction in water consumption intensity over 10 years (excluding farms)
- -22%
reduction in consumption intensity of water for industrial use compared to 2022
An inspiring initiative
The filtering gardens of Saint-Louis
The preservation of natural resources is part of the House’s DNA, and particularly for water, the presence of which determined the installation in 1586 of what would become the Cristalleries Saint-Louis. Today, the production unit is located in the heart of an exceptional territory recognised since 1989 as a cross-border biosphere reserve by UNESCO.

Energy
The group consumes 209,100 MWh of energy (electricity and gas) per year. The majority of the energy (73%) is consumed in industrial activity (cristallerie, tanneries, textiles, leather), while shops and service buildings account for 27% of the total.
Objectives
- Put in place actions compatible with the global warming trajectory of 1.5 degrees and, in particular, continue the decoupling between industrial energy consumption and business growth;
- Implement a policy of 100% renewable electricity within its own operations by 2025 and renewable energies by 2030;
- No longer use gas or any other fossil fuel as an energy source for any new industrial investment, unless shown to be technically impossible;
- Progressively equip all stores with 100%-LED lighting, unless this is technically impossible;
- Contribute to the corporate sobriety effort in the context of major tensions on gas and electricity supplies by reducing energy consumption in France (manufacturing sites, tertiary buildings and stores) by 10% in 2023 compared to 2019.
Results 2023
Evolution of industrial energy consumption (MWh)
In 2023, overall energy consumption decreased compared to 2022 (-4.1%) thanks to the solutions implemented by the manufacturing sites and stores. Over the last decade, the Hermès Group has maintained its ambition of decoupling consumption from growth with a 1.1 fold increase in industrial energy consumption compared with a 3.3 fold rise in activity volumes.
Energy mix
In November 2015, Hermès decided to play an active role in the energy transition process. All its French sites are now supplied with 100% green electricity, from hydroelectric, solar and wind power sources. Worldwide, the group sourced 92% of its electricity from green sources in 2023.
Energy efficiency and optimisation
The most energy-efficient systems have been implemented on production sites, in service buildings and in shops, with insulation, lighting, energy management systems and a choice of energy sources.
The energy efficiency of industrial equipment has been improved by investing in more efficient equipment and reducing consumption by optimising operating parameters. For this reason, more than 80% of the Group’s shops are equipped with LED lighting.
Energy sobriety
Hermès is participating in the national effort to reduce energy use in line with government guidelines for 2022 and 2023, i.e. a target to reduce electricity and gas consumption by 10% in France on an annualised basis. The Group is pursuing the necessary investments to improve its energy efficiency on the one hand, and is working towards carbon-neutral energy on the other. The house has put in place complementary action plans, including shutting down unnecessary equipment at night and on weekends, the reduction of the hourly amplitude of the lighting in store windows and the reduction of the intensity of the lighting according to the activity of its site, optimising the operating ranges of heating and air conditioning, anticipating certain energy performance improvement works and the early renewal of certain equipment.
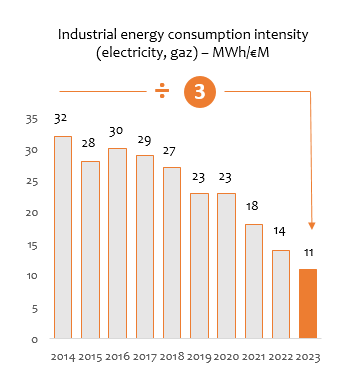
- -65%
reduction in energy consumption intensity over 10 years (excluding farms)
- -51%
in intensity of industrial energy consumption compared to 2019
- >80%
of stores lit with LEDs (worldwide)
- 92%
of electricity from renewable sources (worldwide)
- 5
Leather Goods workshops equivalents using own photovoltaic electricity production
An inspiring initiative
Louviers
Hermès is building the first energy-positive Leather Goods workshop in Louviers (Normandy). The first stone of the production unit was laid in September 2020. This project to rehabilitate a brownfield site near the city centre will serve as a proof of concept for the Hermès group’s future Leather Goods workshops.

Waste
Waste management is a major factor in environmental protection and social responsibility. It requires each of the company’s different métiers to do everything possible to reduce waste production, recover waste or treat it.
The wide diversity of the métiers at Hermès is not conducive to a global policy, aside from the general principle of avoiding the production of waste and working on its end-of-life treatment. Waste management is therefore specifically managed by each industrial division through a dual policy of waste reduction and waste recovery where possible. The main contributors are tanneries, textiles, crystal, leather, perfume and real estate.
Objectives
The House’s policy is based on two main levers:
Reducing waste production
- Innovating across industrial or production management procedures, for example through “exactly enough” as opposed to “surplus” production;
- Leading waste management training and awareness-raising activities, particularly for the offices;
- Reducing the number of unsold items through bespoke commercial management: freedom of purchase for stores, replenishment flexibility and transfers between stores.
Waste recovery
- Facilitating waste collection, and following a circular economy logic, internally and externally, as soon as possible;
- Working on materials end-of-life through the best certified waste treatment channels;
- No destruction of new products intended for sale.
Results 2023
- 12,321
tonnes of ordinary industrial waste (OIW)
- 4,019
tonnes of hazardous industrial waste (HIW)
Reduction of industrial waste in intensity
| 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OIW Intensity (t/M€) | 1.12 | 0.93 | 1.01 |
| Variation | -17% | +8.6% | |
| HIW Intensity (t/M€) | 0,31 | 0,27 | 0,30 |
| Variation | -14% | +11.1% |
Recycling of industrial waste
- 53%
of industrial waste is recycled (excluding energy recovery)
Reprocessing of industrial waste
- 100%
of leather waste from production sites has been processed via approved channels
Recycling of non-industrial waste and awareness-raising among employees
All the House’s sites have introduced waste sorting systems.
All employees have received an eco-action booklet on the prevention of waste production or waste management.
Learn more about
Discover how the resources management takes part in our strategy "All artisans of our sustainable development".
Download our documents:








